Cast iron flat plates are an important tool widely used in precision testing, inspection and marking of the machinery industry. In order to extend the service life of cast iron plates and ensure the accuracy of use, scraping and grinding contact spots is an important technical indicator of cast iron plates.
At present, the evaluation of scratch-and-stain contact spots is considered to be:
First, check the microscopic mass of the working surface of the flat plate, that is, the flatness of the tiny peaks and valleys. The microscopic mass of the surface and good wear resistance can ensure the service life of the flat plate.
The second is to prevent small-scale local distortion on the working surface of the flat plate to ensure the accuracy of the flat plate. The requirements for scraping and grinding contact spots in JJG 117-91 flat panel verification procedures are shown in the following table:
JJG 117-91 Flat plate verification regulations for scraping and grinding contact spots
level | Level 00, Level 0 | Level 1 | Level 2 |
| Scrape the contact spots of the flat plate (25×25 mm) |
Number of spots | ≥25 | ≥20 | ≥12 |
The difference between the number of *** and the number of fewer spots | No more than 5 points |
The above table does not make specific provisions on the area of contact spots (single point area, contact area within unit area) and scraping depth, resulting in different opinions on the evaluation of scraping contact spots.
Reasonable scratching of the contact spots of cast iron plates can extend the service life of the plates. This article discusses the following:
1. Effects of friction on the wear rate of scratching contact spots.
Because the solid surface is rough, the surfaces of the two objects always contact at individual points, so the actual contact area is much smaller than the theoretical contact area. Because the actual contact surface is small, a large unit pressure will be generated even when the load is very small. Due to different surface roughness, the wear of the contact surface also varies with the friction force under unit pressure.
Under the action of unit pressure, the change curve of repeated friction and wear over time is as follows:
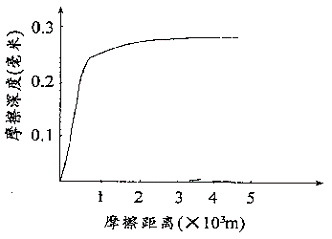
The initial wear amount indicated by the curve is large, which is caused by the unsmooth wear surface, the actual contact area is small, and the specific pressure is large. For flat panels, scraping contact spots during use are always in the initial wear stage, which is one of the main reasons for scraping contact spots. According to the friction speed and contact pressure wear curve (below), it can be seen that when the wear speed v=0.3~0.5m/s, the wear amount is **, which is called adhesive wear. In the use of the flat plate, the movement speed of the workpiece on the flat plate is also working at this stage, which is the second reason for the wear of the scratch contact spots.
In addition, factors such as flat plate material, hardness, environment, maintenance, and maintenance will also have different effects on the wear of scraping and contact spots. In order to study the exact wear conditions of different scraping depths and different contact areas, this article analyzes and discusses them using commonly used test methods and collected data.
2. Determination of scraping depth, scraping contact spot area and analysis of service life of flat plates
The following table is the test data of common cast iron plates in Hebei Botou and cast iron plates in other provinces and cities:
Test
point
number | Scratch depth (μm) | Test
point
number | Scratch depth (μm) | Test
point
number | Scratch depth (μm) | Test
point
number | Scratch depth (μm) | Test
point
number | Scratch depth (μm) |
1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | 35 42 31 37 36 25 36 38 35 36 | 5 8 10 7 5 7 8 11 8 7 | 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | 31 33 46 42 20 52 35 twenty four 31 47 | 8 11 9 6 4 8 10 12 11 10 | twenty one twenty two twenty three twenty four 25 26 27 28 29 30 | 39 49 48 31 41 26 32 32 56 38 | 9 11 10 13 12 9 10 10 10 11 | 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | 37 26 twenty four 34 54 36 41 36 35 54 | 8 10 7 8 10 12 11 11 10 11 | 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 | 50 37 42 45 57 37 32 34 39 37 | 13 10 8 7 5 8 6 9 11 8 |
The contact area of the No. 1 flat plate is 25-27, with a contact area of about 20%; the contact area of the No. 2 flat plate is 25-29, with a contact area of about 10%.
The results of the investigation on the wear of 20 flat plates are: 2 Hebei Botou cast iron flat plates, one for more than 5 years and is still in normal use; the other conductor has been used for more than 5 years, and due to poor storage, rust has been repaired. The remaining 18 cast iron flat plates scraped from other provinces and cities have been used for 1 year. After verification, 10 pieces have been seriously worn and have failed and need to be repaired. 8 pieces can still be used, but some spots have appeared.
The scraping depth is simply processed to obtain its average value. The scraping depth of the No. 1 plate is 37.36 microns, and the scraping depth of the No. 2 plate is 9.06 microns. The difference between the two is as much as three times. According to the relationship between the friction curve loss and the friction time, the plate is always in the initial wear stage, the curve is linear, and the wear amount is proportional to the friction time. Due to the investigation of the wear of the tablet, it can be seen that the service life of Botou tablet in Hebei is 5 times that of the tablet in Wafangdian. It is obvious that the impact of scraping depth on the service life of the tablet cannot be ignored. JJG 117-91 The tablet verification regulations do not stipulate the depth of scraping and grinding, which is undoubtedly a flaw.
From the above test results, it can also be seen that the contact spots of the two are roughly the same, but the measured contact areas are 20% and 10% respectively, which is a huge difference. From the perspective of use, without causing the workpiece to be integrated with the flat plate, the contact area can be increased as much as possible, which can improve the service life of the flat plate. JJG 117-91 flat panel verification regulations also do not properly restrict this item.
In order to improve the service life of the tablet and ensure its working accuracy, it is recommended to control the scraping depth or above 0.02mm, which can ensure that the tablet has a longer service life and calibration cycle. Based on the relevant information, the processing requirements of this process can be achieved.
For the control of contact spot area, the British Standards and Specifications stipulate that the support area ratio of AA (equivalent to JJG 117-91 Procedure Level 0) and A (equivalent to JJG 117-91 Procedure Level 1) plates shall not be less than 20%, and the support area ratio of B (equivalent to JJG 117-91 Procedure Level 2) plates shall not be less than 10%. The high points should be evenly distributed, and the proportion of the supporting area should not be high enough to cause bonding of the workpiece. This regulation ensures the accuracy of the use of the tablet and takes into account the service life of the tablet, which can be learned from it.